Introduction to Environmental Factors and Bronchial Asthma
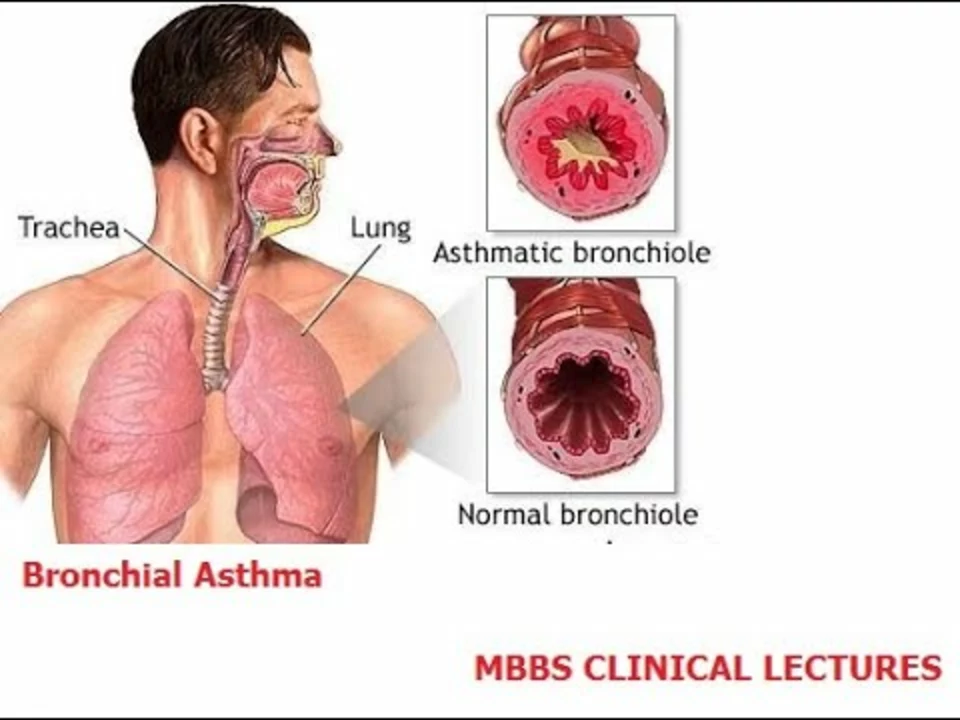
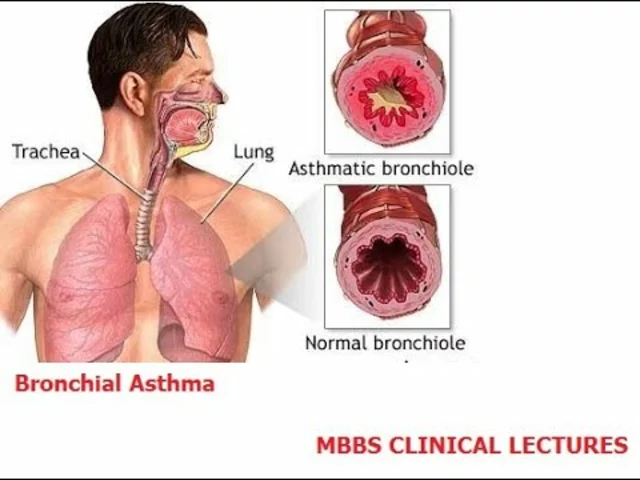
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the airways, making it difficult for people to breathe. Bronchial asthma is triggered by various factors, including those present in the environment. In this article, we will explore the role of environmental factors in bronchial asthma and how they contribute to the development and exacerbation of the condition. We will discuss the most common environmental triggers, ways to reduce exposure, and the importance of managing these factors to improve the quality of life for those living with asthma.
The Impact of Air Pollution on Bronchial Asthma
Air pollution is a significant environmental factor that contributes to bronchial asthma. Pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter can irritate the airways and trigger asthma symptoms. These pollutants are commonly found in areas with high levels of traffic, industrial activity, and urbanization.
Studies have shown that people living in areas with high levels of air pollution are at a greater risk of developing asthma, as well as experiencing more frequent and severe asthma attacks. Reducing air pollution levels through policies and regulations can help to minimize the impact of this environmental factor on asthma sufferers.
Allergens: A Major Environmental Trigger for Asthma
Allergens are substances that can provoke an allergic reaction, causing inflammation in the airways and triggering asthma symptoms. Common allergens include pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and mold spores. Exposure to allergens can cause the immune system to overreact, leading to an asthma attack.
To minimize the impact of allergens on asthma, it's important to identify individual triggers and take steps to reduce exposure. This may include using hypoallergenic bedding, regularly cleaning and vacuuming, and avoiding outdoor activities during peak pollen times.
Climate Change and Its Effect on Asthma
Climate change has been linked to an increase in asthma cases, as well as a worsening of symptoms. Warmer temperatures, more frequent and severe storms, and increased levels of pollen and air pollution all contribute to the exacerbation of asthma symptoms.
Adapting to the effects of climate change and implementing mitigation strategies can help to reduce the impact of these environmental factors on asthma sufferers. This includes promoting clean energy, improving public transportation, and implementing policies to reduce carbon emissions.
Occupational Asthma: A Workplace Concern
Occupational asthma refers to asthma that is caused or worsened by exposure to substances in the workplace. Common triggers include chemicals, dust, fumes, and animal dander. Workers in industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, and construction are at a higher risk of developing occupational asthma.
Employers and employees should be aware of the potential risks and take steps to reduce exposure to these substances. This may include proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and regular health checks for workers with asthma.
Indoor Air Quality and Asthma
Poor indoor air quality can contribute to the development and exacerbation of asthma. Factors such as tobacco smoke, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from cleaning products and building materials, and high humidity levels can all negatively impact indoor air quality.
Improving indoor air quality is essential for managing asthma symptoms. This can be achieved by regularly maintaining heating and cooling systems, using air purifiers, and choosing low-VOC products for cleaning and home improvement projects.
Environmental Tobacco Smoke: A Dangerous Asthma Trigger
Exposure to environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), also known as secondhand smoke, is a well-known trigger for asthma symptoms. ETS contains harmful chemicals that can irritate the airways and cause inflammation, leading to asthma attacks.
Preventing exposure to ETS is crucial for asthma sufferers. This includes implementing smoke-free policies in public places, encouraging smoking cessation, and providing support and resources for those looking to quit smoking.
Managing Environmental Factors for Better Asthma Control
Understanding and managing the environmental factors that contribute to bronchial asthma is essential for improving the quality of life for those living with the condition. By taking steps to reduce exposure to triggers, promoting policies and regulations that minimize the impact of harmful environmental factors, and providing support and education to those affected, we can help to decrease the burden of asthma and promote better health outcomes for all.

Khanyisa Mhlongo
April 30, 2023 at 06:31I live in Johannesburg and the pollen season here is insane lately. My asthma went from manageable to 'why am I coughing into a paper bag' level. They say it's the climate change + urban sprawl combo. Honestly? Feels like the planet is just sighing and giving up. 🌿💨
Leo Lee
April 30, 2023 at 13:11This article reads like a textbook written by someone who's never had an asthma attack. You think telling people to 'avoid pollen' helps when they live in a city with no green space and their landlord won't fix the mold? Wake up. Policy changes. Now.
Chloe McDonald
May 1, 2023 at 04:42My cousin uses an air purifier and it changed her life. Like, she went from missing work every spring to hiking in the mountains. Small stuff adds up.
Hobert Finn Bodfish
May 1, 2023 at 18:48You people are overcomplicating this. Smoke = bad. Pollution = bad. Dander = bad. Clean your house. Stop smoking. End of story. Why are we even having this debate? 😒
Michael Tribone
May 2, 2023 at 01:29I work with asthma kids in after-school programs and honestly? The biggest game-changer is just teaching them and their families what triggers to look for. It’s not magic, it’s awareness. And yeah, clean air matters-but knowing your own body matters more. You got this.
Tracy Blake
May 2, 2023 at 02:44Sometimes I think asthma is just the body's way of screaming, 'Hey, this environment is not a home, it's a hostile takeover!' 🌍💔 We treat the symptoms but ignore the systemic rot-pollution, capitalism-driven urban planning, the fact that poor folks breathe worse air because they can't afford to live anywhere else. We need to stop medicalizing social failure. The lungs don't lie. They just get tired. And so do we.
Manvika Gupta
May 2, 2023 at 17:01in india we have so much smoke from festivals and cars and even cooking fires... my mom has asthma and she just uses a scarf when she goes out. its not ideal but its all she can do. i wish we had better options
Chris Remo
May 3, 2023 at 06:11My buddy’s kid got diagnosed last year. They started using a HEPA filter, switched to fragrance-free stuff, and now the kid’s in soccer. No inhaler needed most days. Small wins, people. They count.
Stephanie Cepero
May 4, 2023 at 05:07I just want to say... thank you for writing this. My daughter’s asthma got worse during the wildfires last year, and I felt so helpless. This isn’t just about medicine-it’s about justice. People deserve clean air. I’m sharing this with my PTA.
Daniel Rogers
May 5, 2023 at 04:24I used to think asthma was just 'bad luck'... until my neighbor’s kid had a hospital visit every time the wind blew from the highway side. Now I get it. It’s not luck. It’s location. And that’s not fair. 🙏
Andrea Galetto
May 5, 2023 at 06:43If you're too lazy to clean your house or quit smoking, don't blame the government. Personal responsibility is not a myth. This article is a luxury for those who have the privilege to care. Most people just want to breathe without a lecture.
Isabel Piaggi
May 6, 2023 at 06:21i read this and i just wanna cry not because im sad but because its so true and nobody listens like seriously why do we keep building houses next to highways and call it progress i mean like the air here smells like a diesel truck threw up and i have to use my nebulizer just to watch tv at night 😔
Tom McInnes
May 6, 2023 at 09:23The data is clear. Environmental triggers are modifiable risk factors. The question isn’t whether we can act-it’s whether we have the collective will. I’d recommend reviewing WHO’s 2022 guidelines on air quality and asthma management. They’re accessible.